Education: 4 C'S
The Four C's
Where else can you buy a billion-year-old item and wear it every day? No two diamonds are exactly the same — these are just a few of the things that make diamonds so special. Before selecting a diamond for your custom engagement ring, it’s important to understand the 4Cs; a standardized grading system that rates the cut, color, clarity, and carat weight of a stone. Here are the basics.
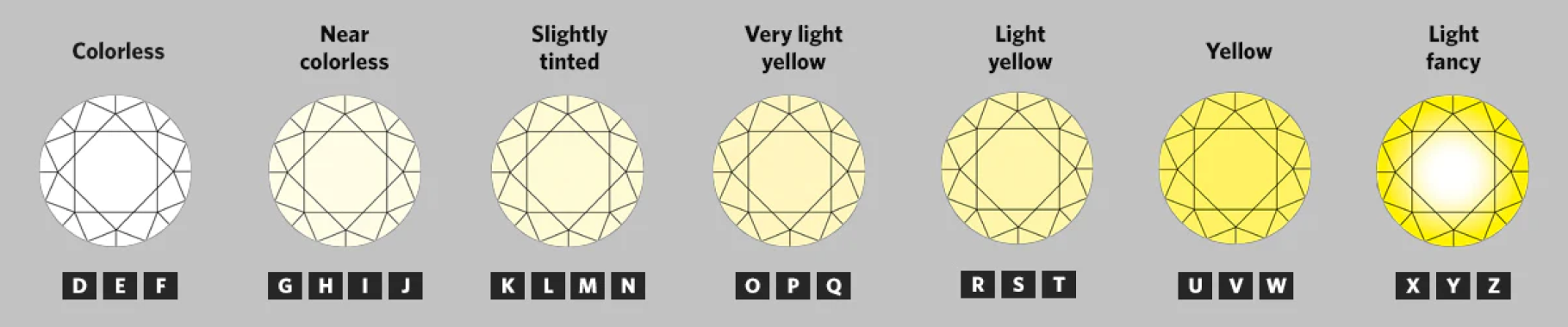
COLOR
Color is evaluated through the absence of color, which can be difficult to see with the naked eye. The color grading scale assigns every diamond a rating.
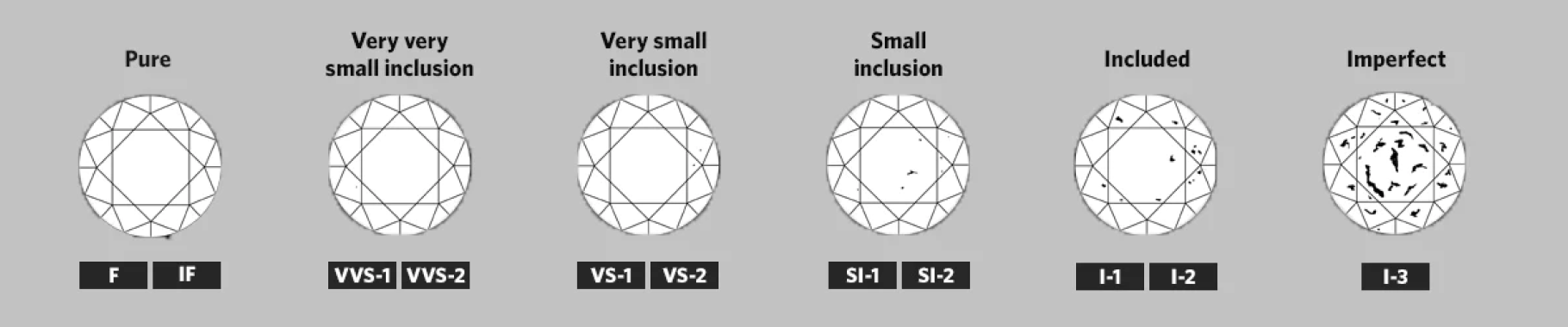
CLARITY
Clarity refers to the absence of inclusions and blemishes. When a diamond forms, it is exposed to mass amounts of heat and pressure within the Earth. This causes internal characteristics, known as inclusions, and external characteristics called blemishes. Clarity is evaluated by identifying the number, size, nature, and position of the inclusions and blemishes. No diamond is completely pure, but the closer to perfection, the higher the value.
CUT
Cut refers to how well a stone refracts light within the facets. Precise artistry and workmanship are responsible for a diamond’s proportions, symmetry and polish. We consider the cut to be one of the most important aspects when looking for a beautiful, sparkly diamond.

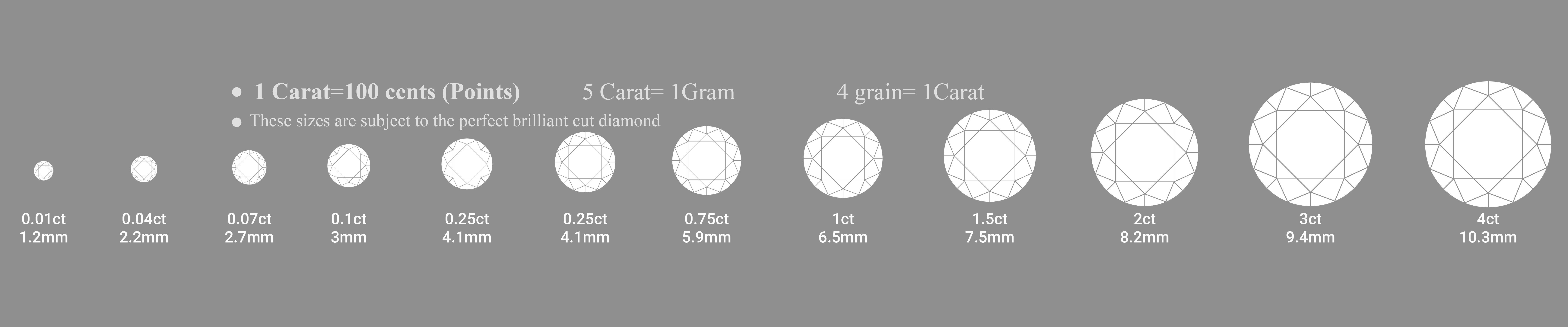
CARAT
Carat weight is the measurement of a diamond’s weight. One carat equals 200 milligrams, and each carat represents 100 points. Jewelers will often refer to carat weight by its points. For example, a diamond that weighs .25 carat may be called a 25 pointer. Anything larger than a carat is represented by a decimal, such as 1.25 carats. Since the carat represents the weight and not the dimensions, a 1 carat diamond may look different visually depending on where the weight of the stone is and how well it is cut.